A burning question for Python newbies coming from C, Perl, Bash or other programming languages who have this statement or function. To answer "Python has a print function and no printf function" is only one side of the coin or half of the truth. One can go as far as to say that this answer is not true.
No, but the functionality of the "ancient" printf is contained in Python. To this purpose the modulo operator "%" is overloaded by the string class to perform string formatting. Therefore, it is often called string modulo operator, though it has not a lot in common with the actual modulo calculation on numbers.
Another term for it is "string interpolation", because it interpolates various class types into a formatted string. In many cases the string created via the string interpolation mechanism is used for outputting values in a special way. But it can also be used, for example, to create the right format to put the data into a database.
Since Python 2.6 has been introduced, the string method format should be used instead of this old-style formatting. Unfortunately, string modulo "%" is still available in Python3 and what is even worse, it is still widely used. That's why we cover it in great detail in this tutorial. You should be capable of understanding it, when you encounter it in some Python code. However, it is very likely that one day this old style of formatting will be removed from the language. Sometimes, we may wish to print multiple values in a Python program in a readable manner.
The arguments passed to the program can be separated by different values. The sep parameter is primarily used to format the strings that need to be printed on the console and add a separator between strings to be printed. This feature was newly introduced in Python 3.x version. Computer programmers often require the ability for their programs to create character strings at runtime.
These strings may include variables of a variety of types, the exact number and order of which are not necessarily known to the programmer during development. The widespread need for flexible string creation and formatting routines naturally lead to the development of the printf family of functions. The printf functions create and output strings formatted at runtime.
Additionally, the printf functionality is implemented in other languages . The printf function will then convert the binary value to a character representation based on the format specifier and include it as part of the formatted output string. As will be demonstrated, this occurs regardless of whether the programmer has actually passed a second argument to the printf function or not. Because the function does not know how many arguments it will receive, they are read from the process stack as the format string is processed based on the data type of each token. In the previous example, a single token representing an integer variable was embedded in the format string.
The function expects a variable corresponding to this token to be passed to the printf function as the second argument. On the Intel architecture , arguments to functions are pushed onto the stack before the stack frame is created. When the function references its arguments on these platforms, it references data on the stack beneath the stack frame. For example, the statement print('hello' + 'world') prints helloworld without the added empty space separator character. The values mentioned above can be any string or any of the data types like list, float, string, etc. The other arguments include a separator used to divide the values given as arguments whereas the argument end is the \n newline character by default.
This is the reason why whenever the print() function is called, the cursor slides to the next line. As we will see, the ability for an external source to control the internal function of a printf function can lead to some serious potential security vulnerabilities. If a program exists that contains such a bug and returns the formatted string to the user , attackers can read possibly sensitive memory contents. Memory can also be written to through malicious format strings by using the obscure format specifier %n. The purpose of the %n token is to allow programmers to obtain the number of characters output at predetermined points during string formatting.
How attackers can exploit format string vulnerabilities will be explained in detail as we work toward developing a functional format string exploit. Often you'll want more control over the formatting of your output than simply printing space-separated values. The string types have some methods that perform useful operations for padding strings to a given column width; these will be discussed shortly. The comma-separated parameters that follow (ie, k, freq) supply the interpreter with the string and the number that will be used in the execution of the printf command. Format commands are short routines built into many programming languages, that display variables as neat columns of padded or justified words and numbers. Format commands have equivalent functionality in most higher level programming languages .
The following the list of specifiers constitute the most common instructions in printf statements. In the program written above, the elements of a list are stored in a variable called listfruits. A for loop is executed to iterate over the elements and print them out one by one.
You can see that an end argument is passed along with the print statement. This avoids the strings to be printed on different lines. We add space in string in python by using rjust(), ljust(), center() method.
To add space between variables in python we can use print() and list the variables separate them by using a comma or by using the format() function. In this tutorial, we will be discussing how to add space in python. Adding space between variable, string increase the readability while displaying the output of the program.
We can add space in python between two variables, strings, and lines. The methods of Python's str type give you a powerful set of tools for formatting, splitting, and manipulating string data. But even more powerful tools are available in Python's built-in regular expression module. In this example, we will take a string with chunks separated by one or more single space characters. Then we shall split the string using re.split() function.
You can modify the spacing between the arguments of the print statement by using the sep parameter. The sep parameter can only be found and used in Python 3 and later versions. It can also be utilized for the formatting of the output strings.
The sys.stdout is a file object that is used for displaying the output of a print statement. The sys.stdout.write() method does not add a newline at the end of a string to be displayed. Filenames are passed to and returned from APIs as strings. This can present platform-specific problems because on some platforms filenames are arbitrary byte strings. Thus, os.listdir() returns a list of bytes instances if the argument is a bytesinstance, and os.getcwdb() returns the current working directory as a bytes instance. Note that whenos.listdir() returns a list of strings, filenames that cannot be decoded properly are omitted rather than raisingUnicodeError.
In this article, we have explored the different ways by which values can be printed without a newline character/carriage return. This strategy can come quite handy while printing the elements in the outputs of algorithms such as a binary tree or printing the contents of a list next to each other. In many applications a separate control character called "manual line break" exists for forcing line breaks inside a single paragraph. The glyph for the control character for a hard return is usually a pilcrow (¶), and for the manual line break is usually a carriage return arrow (↵). We will take a simple code for all the methods, which takes up a print statement and contains several arguments separated by commas. For example, the following program below uses the comma operator to print the values.
To add space in python, at both ends of the string we use center() method. The length is increased by adding characters on both sides of the original string. Another way to remove spaces in multiple print argument is using sepoption of the printfunction. In this example we use empty string as separator which will join two string together.
I have a simple problem with python about new line while printing. In python printwill add at the end of the given string data \nnewline or a space. But in this situation we do not will use appendstring to stdout. Here we've first compiled a regular expression, then used it to split a string. One place where the Python language really shines is in the manipulation of strings.
Such string manipulation patterns come up often in the context of data science work, and is one big perk of Python in this context. Strings are arrays of bytes in Python that represent Unicode characters. However, because Python lacks a character data type, a single character is merely a one-length string.
One can use Square brackets can be used to access the string's elements. Rather than have users be constantly writing and debugging code to save complicated data types, Python provides a standard module called pickle. This is an amazing module that can take almost any Python object (even some forms of Python code!), and convert it to a string representation; this process is called pickling. Reconstructing the object from the string representation is called unpickling.
Between pickling and unpickling, the string representing the object may have been stored in a file or data, or sent over a network connection to some distant machine. In our example, an argument was passed to the printf function corresponding to the %i token—the integer variable. The Base10 character representation of the value of this variable was output where the token was placed in the format string. This format string argument consists of static text and a token (%i), indicating variable data. In this example, the value of this integer variable will be included, in Base10 character representation, after the comma in the string output when the function is called. The one-liner Perl command saves 10 spaces for a string, printing the string from left to right, beginning with the first space.
If you want to remove all the duplicate whitespaces and newline characters, then you can use join() function with string split() function. If set to the string '1.21' enables 1.21 legacy printing mode. This approximates numpy 1.21 print output of complex structured dtypes by not inserting spaces after commas that separate fields and after colons.
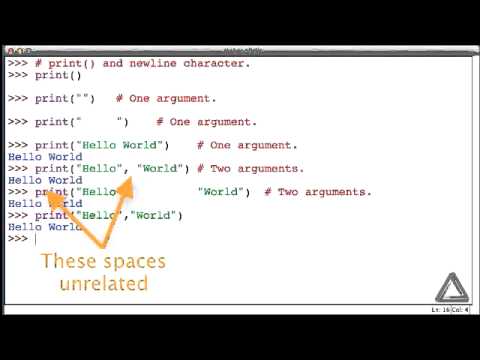
So here in the above example, Python by default gives the value of the argument sep, a blank space. Python also adds a newline character at the end, hence we can see that the interpreter prompt goes to the next line. Strings are a sequence of letters, numbers, symbols, and spaces. Strings are an important data type in most programming languages, especially Python. When you're working with strings, there are many cases where you will want to make them more readable through punctuation, adding new lines, or moving text onto the same lines. Every running program has a text output area called "standard out", or sometimes just "stdout".
The Python print() function takes in python data such as ints and strings, and prints those values to standard out. To add space in python, at the end of the string we use ljust() method. The length is increased by adding character at the right side of the original string. We are printing two strings, so Python will use the value of sep, a blank space by default, to print them together. Python also adds a newline character at the end, so the interpreter prompt goes to the end line.
In summary, we learnt different methods to remove spaces within a string and also methods to remove spaces from the beginning and end of a string. You now have a sufficient number of options for replacing or removing white spaces from Python strings. This is a list of the standard printf functions included in the standard C library.
Each of these can lead to an exploitable format string vulnerability if misused. If you want to get rid of all the duplicate whitespaces and newline characters, then you can use join() function with string split() function. This string has different types of whitespaces as well as newline characters. In this tutorial of Python Examples, we learned how to split a string by space using String.split() and re.split() methods. Also, we learned how to split a string by considering all whitespace characters as delimiter.
In this example, we will take a string which contains words/items/chunks separated by space character. We shall then split the string by space using String.split() method. In this tutorial, we will learn how to split a string by a space character, and whitespace characters in general, in Python using String.split() and re.split() methods. The following code uses the fstring formatting to print without spaces between values in Python. This can be tedious to write—and it may not be the most efficient solution due to the repeated creation of a new string based on two old string objects. Python 3 provides simple and convenient solution for this issue.
Printfunction provides more than string to be printed. Endparameter is used to specify the line end character. We will set endoption to nothing and this will remove default \nor end of line or space.
These special characters match specified groups of characters, and we've seen them before. In the email address regexp from before, we used the character "\w", which is a special marker matching any alphanumeric character. Similarly, in the simple split() example, we also saw "\s", a special marker indicating any whitespace character. When this function executes, it does not know that there has not been a variable passed corresponding to the %i token. Python NumPy module has numpy.core.defchararray.rstrip method to remove all the trailing white-spaces from every element of the input array.





























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.